Welding is one of the primary methods for permanently joining two or more metal parts, widely used in various industries such as construction, automotive, shipbuilding, oil and gas, and many others. The welding process largely depends on the type of welding electrodes used. This article delves deeper into the different types of welding electrodes, their various classifications, welding processes, and the diverse applications of these processes.
Welding is performed using various methods, each selected based on specific industrial needs and conditions. Some of the most important welding processes include:
Arc Welding:
This method uses an electrode to create an electric arc, which melts the metals and forms the weld. It includes several subcategories:
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW): Also known as stick welding, this is one of the most common welding methods. It utilizes a metal electrode coated with a protective layer that melts during welding, forming the weld while providing shielding from environmental contaminants.
MIG/MAG (Metal Inert Gas/Metal Active Gas) Welding: This method employs a continuously fed wire electrode shielded by an inert or active gas (usually argon or a mixture of gases) to protect the weld from oxidation. It is especially useful for welding non-ferrous metals and stainless steel.
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) Welding: This process uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode. The weld is protected by an inert gas (usually argon), making it ideal for precision and clean welding of thin materials like aluminum and stainless steel.
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW):
In this method, the electrode and the electric arc are submerged under a protective flux powder. It is used for welding large and heavy metal components that require deep penetration, providing high-quality welds due to the complete protection of the arc and weld.
Spot Welding:
Commonly used in the automotive industry, this method welds thin metal sheets by applying pressure and electric current through two electrodes, creating a spot weld.
Plasma Arc Welding (PAW):
This method uses a plasma arc for welding, capable of producing very high temperatures. It is suitable for welding extremely thin and heat-sensitive metals.
Laser Welding:
Laser welding utilizes a laser beam to generate heat and melt the metals. Due to its high precision and control, it is used in sensitive industries like aerospace and medical equipment.
Underwater Welding:
This type of welding is used for the repair and maintenance of underwater structures such as docks, pipelines, and ships. Underwater welding can be performed either dry (in pressurized chambers) or wet (directly in water).
Friction Welding:
This method joins two metal parts through rapid rotation and pressure, generating heat through friction, which softens the metals and facilitates their bonding. It is highly effective for welding round and cylindrical parts.
Welding electrodes are broadly classified into two categories: consumable and non-consumable.
Consumable Electrodes:
These electrodes melt during the welding process, becoming part of the weld itself. They are typically made from metals like steel, nickel, or aluminum and also serve as filler material.
Types of Consumable Electrodes:
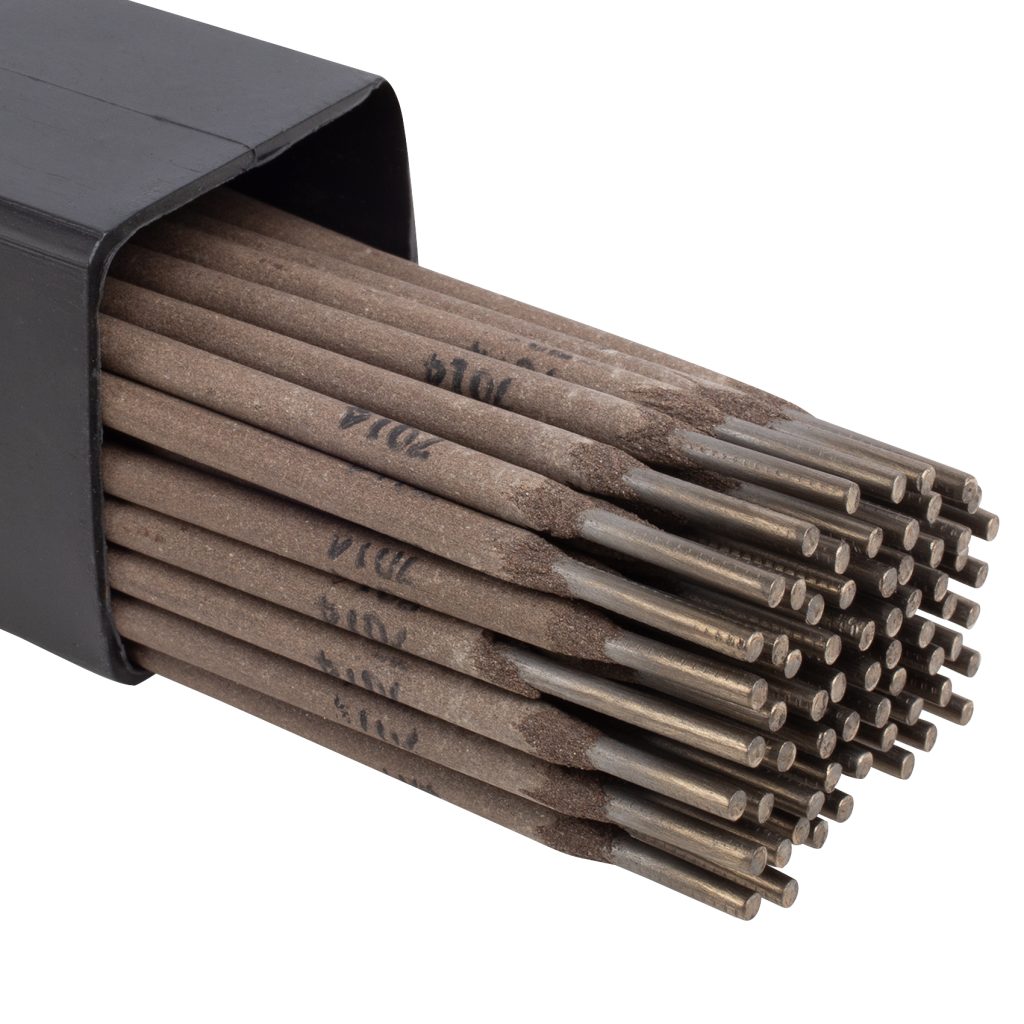
Shielded Metal Arc Welding Electrodes (SMAW): These electrodes are coated with a layer of minerals or cellulose, which melts during welding and protects the weld from environmental contaminants. Various types of these electrodes are designed for different conditions and metals.
Welding Wires: These electrodes come as continuous wires and are used in semi-automatic welding processes like MIG/MAG and Submerged Arc Welding. The composition of these wires varies depending on the type of metal being welded and the working conditions.
Flux-Cored Wires: These electrodes have a core filled with powder that converts to shielding gas during welding, eliminating the need for an external shielding gas.
Non-Consumable Electrodes:
These electrodes do not melt during the welding process and are primarily used to conduct electric current and create the arc.
Types of Non-Consumable Electrodes:
Welding electrodes are available in different types based on their chemical composition and coating. Some well-known types include:
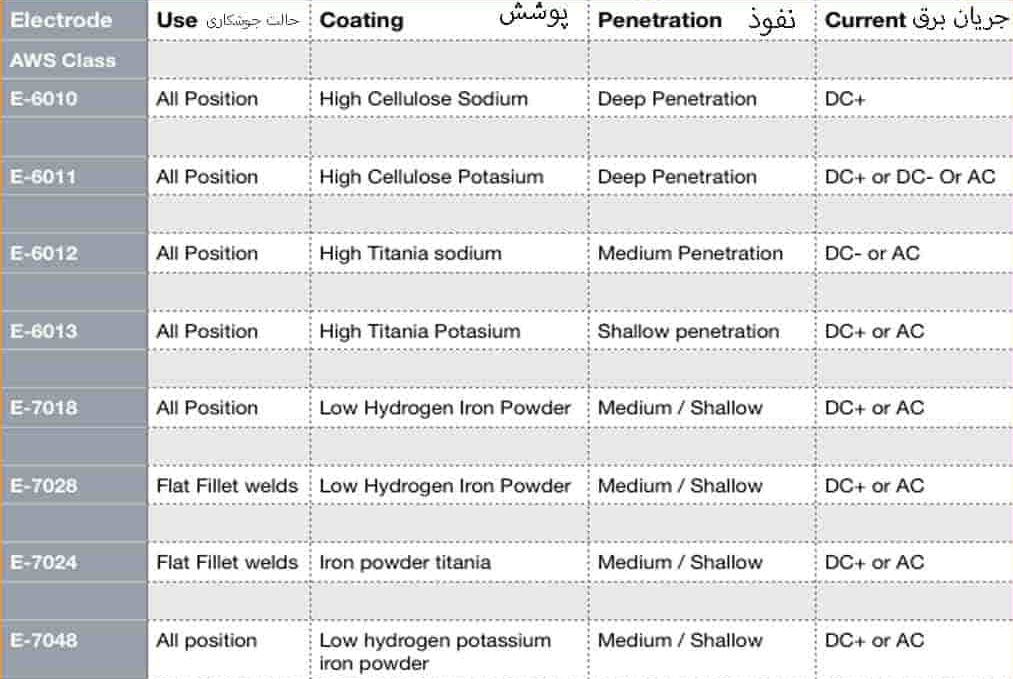
E6010: Suitable for welding in all positions, this electrode provides deep penetration and is widely used in pipe welding and heavy structures.
E6011: Similar to E6010 but can be used with AC current as well.
E6013: Ideal for light welding tasks and home use, this electrode offers shallow penetration and easy application.
E7018: A low-hydrogen electrode used for welding low-alloy steels and crack-resistant joints, commonly employed in constructing sensitive and heavy structures.
Welding and the use of welding electrodes have extensive applications across various industries:
Construction Industry: Welding plays a crucial role in constructing buildings, bridges, towers, and other steel structures. The choice of welding electrodes depends on the type of structure and environmental conditions.
Oil and Gas Industry: Pipeline welding in the oil and gas sector requires highly durable and precise welds. Electrodes with deep penetration, such as E6010 and E7018, are commonly used in this industry.
Automotive Industry: In this sector, welding is used for joining car body parts and chassis using various welding methods, including spot welding and MIG/MAG welding.
Shipbuilding and Marine Industry: Underwater welding and corrosion-resistant welding are essential for repairing and maintaining ships and marine structures.
Aerospace Industry: The aerospace industry demands precision and lightweight welding for manufacturing sensitive and complex parts. Techniques like laser welding and TIG welding are widely used.
Light Industry and Home Use: Home repairs and small-scale welding tasks typically use simple electrodes like E6013, known for their easy application and low cost.
For professional project management, procurement, and execution of welding-related services, Rasta Company stands ready to offer its expertise as an EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) contractor. Backed by extensive experience and technical know-how, Rasta can assist in selecting the most suitable electrodes and executing welding projects across various industries, ensuring compliance with all relevant standards and delivering high-quality results.



Welding electrodes, due to their direct impact on the quality and strength of welds, are produced and evaluated under various international and national standards. These standards are developed to ensure quality, safety, and efficiency under different welding conditions. The most important standards related to welding electrodes include:
1. AWS (American Welding Society) Standards
AWS standards are among the most important and reputable global standards in the field of welding. They specify technical specifications and criteria for different types of electrodes. Some well-known AWS codes for welding electrodes include:
– AWS A5.1: This standard covers carbon steel electrodes for Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW). Electrode classifications such as E6010, E6011, E6013, and E7018 fall under this standard.
– AWS A5.18: This standard covers carbon steel filler metal for MIG/MAG welding.
– AWS A5.28: This standard applies to low-alloy steel electrodes for MIG/MAG welding.
– AWS A5.32: This standard pertains to tungsten electrodes used in TIG welding.
2. ISO (International Organization for Standardization) Standards
ISO standards also play a crucial role in the field of metal welding electrodes. Some relevant ISO standards include:
– ISO 2560: This standard applies to covered electrodes for manual metal arc welding (SMAW) of non-alloy and fine-grain steels.
– ISO 14341: This standard is for welding filler wires of non-alloy and low-alloy steel for welding with protective gases (MIG/MAG).
– ISO 6847: This standard specifies requirements for non-consumable tungsten electrodes used in TIG welding.
3. EN (European Norms) Standards
EN standards are recognized in Europe as key benchmarks for the production and evaluation of welding electrodes:
– EN 499: European standard for covered electrodes for manual metal arc welding (SMAW) of non-alloy and fine grain steels.
– EN 440: This standard pertains to steel filler wires for MIG/MAG welding.
– EN ISO 636: European standard for non-consumable tungsten electrodes used in TIG welding.
4. National Standards
In addition to international standards, some countries have their own national standards governing the production and use of welding electrodes. For example:
– ISIRI (Institute of Standards and Industrial Research of Iran): The ISIRI has national standards for welding electrodes, such as ISIRI 424, which applies to covered carbon steel electrodes.
The selection of the appropriate welding electrode should be made considering the existing standards and working conditions. For any welding project, the technical specifications of the electrode (such as chemical composition, diameter, type of coating, and required electrical current) must comply with relevant standards to ensure the quality and durability of the weld.
Rasta Company, leveraging its extensive technical expertise and experience in engineering, procurement, and execution of welding projects, is ready to operate as an EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) contractor in the field of welding electrodes. The company is capable of providing high-quality and committed services to its clients, from selecting the most suitable electrodes to the complete execution of welding projects, all in compliance with international and national standards.
With a team of specialists and advanced equipment, Rasta can undertake welding projects in various industries, including oil and gas, petrochemicals, construction, and automotive. Partnering with Rasta ensures the success and durability of your welding projects.
For inquiries, purchasing, or more information about our products, please reach out to us using the contact details below:
– Phone: +98 21 8877 0680
– WhatsApp: +98 912 6835 639
– Telegram Group: SAVA Business Group
Our team is dedicated to providing excellent support and is ready to assist with any questions or needs you may have.
