Inverters play a critical role in solar energy systems, acting as a bridge between solar panels and the electrical grid or load. Their primary function is to convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is the standard form of electricity used in most household appliances and the electrical grid. This article explores the types, functions, benefits, and importance of solar inverters in optimizing solar energy systems.
1. String Inverters
String inverters are the most common type of solar inverters. They work by connecting several solar panels in series (or “strings”) and then converting the combined DC electricity from the string into AC electricity. Key features include:
2. Microinverters
Microinverters are small inverters attached to each individual solar panel. They convert DC electricity to AC at the panel level and offer several advantages:
3. Power Optimizers
Power optimizers work alongside string inverters. They are installed at the panel level to optimize the performance of each solar panel before sending DC electricity to the central inverter:
4. Hybrid Inverters
Hybrid inverters, also known as battery-based inverters, are designed to work with both solar panels and energy storage systems (batteries). They manage solar energy production, battery storage, and grid interaction:
1. DC to AC Conversion
The primary function of a solar inverter is to convert the DC electricity produced by solar panels into AC electricity, making it usable for household appliances or the electrical grid.
2. Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)
Inverters use MPPT technology to optimize the efficiency of solar systems. MPPT continuously monitors the output of solar panels and adjusts the electrical load to maximize energy production.
3. Monitoring and Communication
Modern solar inverters often come with monitoring capabilities that allow users to track the performance of their solar system in real time. This data can be accessed through online platforms or mobile apps, providing insights into energy production and system health.
4. Grid Compliance and Safety
Inverters ensure that the electricity produced by solar panels meets grid safety and compliance standards. They include features such as anti-islanding protection to prevent the continuation of power supply during a grid outage.
1. Enhanced Efficiency
Solar inverters enhance the overall efficiency of solar energy systems by ensuring maximum conversion of solar energy into usable electricity. Advanced technologies like MPPT further optimize performance.
2. Cost Savings
By converting solar energy into usable electricity or selling it back to the grid, solar inverters help reduce electricity bills and provide financial returns through net metering programs.
3. Improved System Performance
Using microinverters or power optimizers can improve system performance by minimizing the effects of shading and panel mismatch. This results in more consistent energy production and better system reliability.
4. Energy Independence
Hybrid inverters facilitate energy storage, allowing homeowners to store excess solar energy for use when sunlight is not available. This contributes to greater energy independence and resilience.
5. Environmental Benefits
Solar inverters play a crucial role in promoting renewable energy use, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. By efficiently converting solar energy, inverters support the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
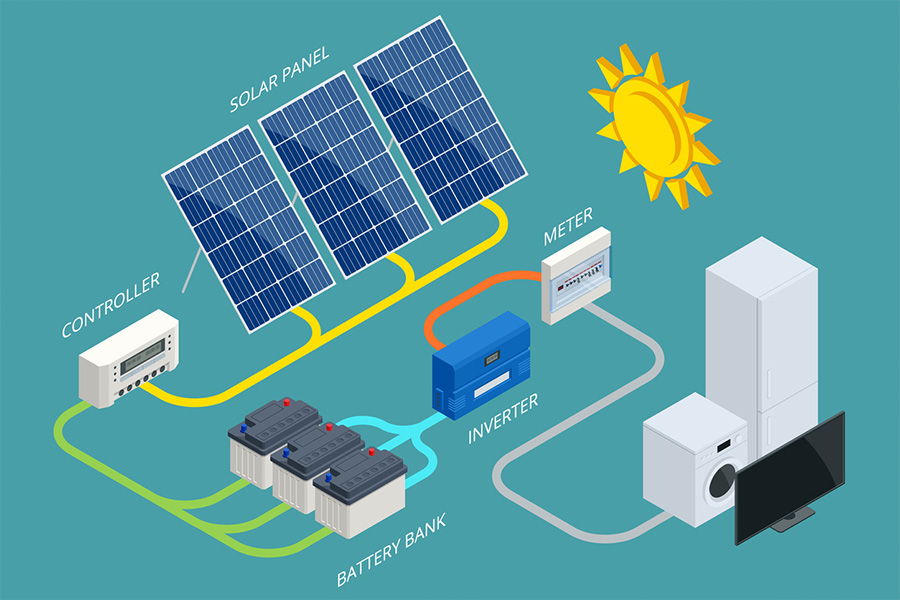

Solar inverters must be designed and manufactured according to national and international standards to ensure their performance, safety, and compliance with grid regulations. These standards include technical, safety, and performance requirements, and various tests are essential to assess them. Below is an overview of key standards and tests related to solar inverters:
IEC 62109
IEC 61727
IEC 60068
UL 1741
IEEE 1547
Safety Tests
Performance Tests
Durability Tests
Power Quality Tests
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Testing
After conducting tests, detailed testing reports are provided, including precise results, deviations from standard requirements, and recommendations for improvements to manufacturers. These reports assist in confirming the quality and safety of products and are essential for ensuring compliance with international and national standards. Certifications related to standards and testing are necessary for the sale and installation of inverters in various markets.
Rasta Development and Trading Innovators proudly announces its capability to supply a wide range of solar inverter brands with the highest quality and in accordance with international standards. With over two decades of experience in manufacturing and exporting industrial products, we have earned the trust and satisfaction of our customers both domestically and internationally.
Our services include:
Diverse Inverter Brands Supply: We can supply solar inverters from renowned global brands with varied technical specifications and quality levels. By closely collaborating with leading manufacturers, our products ensure top-notch performance, durability, and efficiency.
Adherence to International Standards: All inverters supplied by our company comply with internationally recognized standards, including IEC, UL, and IEEE. These standards cover safety, performance, and grid compatibility requirements, ensuring the quality and safety of our products.
Export Licenses: Rasta Development and Trading Innovators holds all necessary licenses for exporting solar inverters to various global markets. These licenses include certifications for international standards and required approvals for entry into international markets.
Global Shipping: Utilizing reputable and experienced transportation networks, we offer logistics and shipping services worldwide. Our products are dispatched to various destinations with secure packaging and transportation practices.
At Rasta Development and Trading Innovators, leveraging our specialized team and advanced technologies, we continuously strive to provide the best services and products to our customers. Your trust is our asset, and we prioritize quality and satisfaction.
For more information and to place orders, please contact us:
Phone and WhatsApp: +98 912 683 5639
Landline (Vank Office): +98 21 8877 0680
Address (Vank Office): Vank Street, No. 27, Unit 1
Email: Info@rastaexport.com
Telegram Channel: SAVA Commercial Enterprise
Join us and benefit from our top-quality solar inverter supply and export services, adhering to the highest international standards.
