
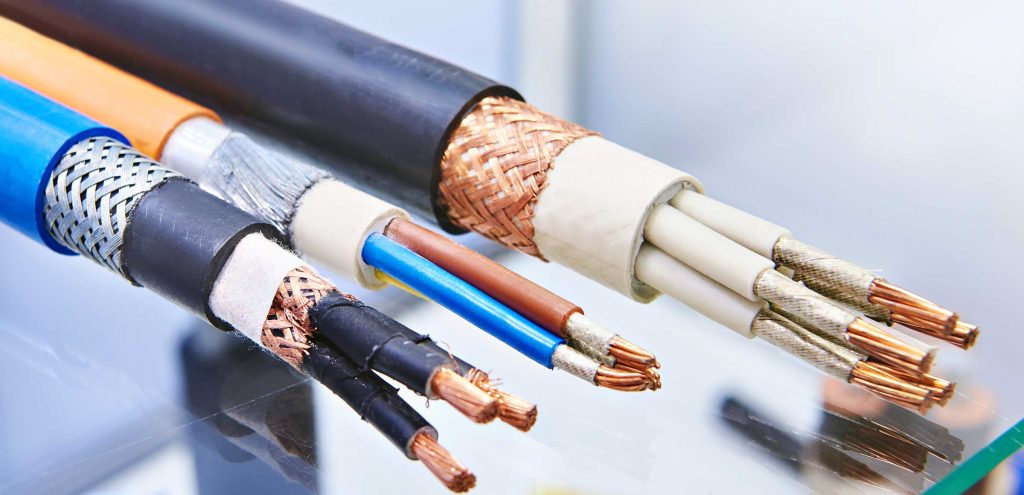
A cable is an electrical device used to transmit electrical energy or data from one point to another. Cables are composed of several main components, each playing a specific role in the cable’s performance. These components include the conductor (usually made of copper or aluminum), insulation, shield (in some cables), and outer jacket.
1. Conductor: The conductor is the main part of the cable that transmits electrical current or signals. Conductors are usually made of copper or aluminum due to their high conductivity.
2. Insulation: Insulation separates the conductor from the external environment and other conductors, preventing short circuits. Insulations are typically made from plastic materials such as PVC or PE.
3. Shield: The shield is a metallic layer used in some cables to protect the signals from electromagnetic interference (EMI). The shield can be woven, foil, or a combination of both.
4. Outer Jacket: The outer jacket or sheath protects the entire cable from mechanical damage, moisture, and chemicals. This jacket is usually made from durable materials like PVC or polyethylene.
Cables are used in many industries and everyday applications. From power cables supplying electrical energy in homes and industries to network cables connecting computers and other devices to the internet, cables play a vital role in modern life. Additionally, telecommunication and fiber optic cables are used for high-speed data transmission in communication networks. Audio and video cables are also used to connect playback devices and displays.
Cables are categorized into different types, each designed for specific applications. Below are some types of cables:
– Low Voltage (LV) Cables
– Medium Voltage (MV) Cables
– High Voltage (HV) Cables
– Telephone Cables
– Fiber Optic Cables
– Ethernet Cables (Cat5, Cat6, Cat7)
– Fiber Optic Cables
– RG-6
– RG-59
– Multi-core Cables
– Shielded Cables
– HDMI Cables
– VGA Cables
– RCA Cables
– USB Cables
– Lightning Cables
– USB-C Cables
Power cables are used to transmit electrical energy from one point to another. These cables are divided into three main categories: Low Voltage (LV) Cables, Medium Voltage (MV) Cables, and High Voltage (HV) Cables. Low Voltage Cables are typically used in residential and small commercial applications with voltages up to 1000 volts. Medium Voltage Cables are used for power distribution in local and industrial networks with voltages between 1 kV to 35 kV. High Voltage Cables are used for long-distance power transmission with voltages higher than 35 kV. Each of these cables has specific features such as insulation, heat resistance, and moisture resistance, making them suitable for specific applications.
Telecommunication cables are used to transmit data and information. These cables include telephone cables and fiber optic cables. Telephone cables are usually made of copper and are used for transmitting voice signals and low-volume data. These cables are used in telephone networks and old communication systems. Fiber optic cables are made of glass or plastic and are used for high-speed data transmission over long distances. These cables are used in internet networks, cable television, and advanced communication systems due to their high bandwidth and resistance to electromagnetic interference. Fiber optic cables are divided into single-mode and multi-mode types, each suitable for specific applications.
Network cables are used to connect various devices in a computer network. These cables include Ethernet cables (Cat5, Cat6, Cat7) and fiber optic cables. Ethernet cables are usually made of copper and are used for data transmission in local area networks (LAN). These cables are divided into different categories, each with different bandwidth and data transfer speeds. For example, Cat5e cables are suitable for speeds up to 1 Gbps, while Cat6 and Cat7 cables are suitable for higher speeds up to 10 Gbps. Fiber optic cables are also used in larger networks and for long-distance data transmission. These cables are used in internet networks and data centers due to their high bandwidth and resistance to electromagnetic interference.
Coaxial cables are used to transmit radio, television, and internet signals. These cables include various types such as RG-6 and RG-59. RG-6 cables are used for high-quality television and internet signal transmission and are commonly used in cable TV and satellite systems. These cables have better insulation and lower resistance compared to RG-59 cables. RG-59 cables are used for video and audio signal transmission in surveillance systems and CCTV cameras. These cables are suitable for installation in confined spaces due to their smaller diameter and greater flexibility. Both types of coaxial cables have a central copper core, an insulation layer, a metallic shield, and an outer jacket that protects them from electromagnetic interference.
Control and instrumentation cables are used to transmit control signals and precise data in industrial and automation systems. These cables include multi-core cables and shielded cables. Multi-core cables have several separate conductors, each used for transmitting different signals. These cables are used in control systems, industrial machinery, and automation equipment. Shielded cables have a metallic shield layer that protects them from electromagnetic interference. These cables are suitable for transmitting sensitive and precise signals in high-noise industrial environments. Both types of control and instrumentation cables have features such as heat resistance, moisture resistance, and chemical resistance, making them suitable for industrial applications.
Audio and video cables are used to transmit audio and video signals between different devices. These cables include HDMI, VGA, and RCA cables. HDMI cables are used for high-quality digital audio and video signal transmission and are commonly used in televisions, monitors, and video playback devices. These cables can transmit 4K and even 8K signals. VGA cables are used for analog video signal transmission and are commonly used in monitors and projectors. These cables are less commonly used in new devices due to their lower quality compared to HDMI. RCA cables are used for analog audio and video signal transmission and are commonly used in old audio and video devices such as televisions and DVD players. These cables have three colored connectors (red, white, and yellow), each used for transmitting a specific type of signal.
Charging and data transfer cables are used to charge electronic devices and transfer data between them. These cables include USB, Lightning, and USB-C cables. USB cables are used to connect various devices to a computer transfer data and charge them. These cables are divided into different types such as USB 2.0, USB 3.0, and USB 3.1, each with different data transfer speeds and charging capacities. Lightning cables are used for Apple devices such as iPhones and iPads and can transfer data and charge devices at high speeds. USB-C cables are the newest type of charging and data transfer cables with a reversible connector and the ability to transfer data and charge devices at high speeds. These cables are used in new devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets and are quickly replacing older cables due to their multiple capabilities and high speed.

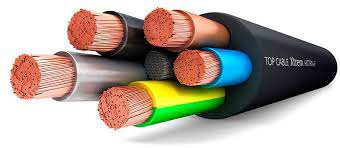

A cable is an electrical device used to transmit electrical energy or data from one point to another. Cables are composed of several main components, each playing a specific role in the cable’s performance. These components include the conductor (usually made of copper or aluminum), insulation, shield (in some cables), and outer jacket.
1. Conductor: The conductor is the main part of the cable that transmits electrical current or signals. Conductors are usually made of copper or aluminum due to their high conductivity.
2. Insulation: Insulation separates the conductor from the external environment and other conductors, preventing short circuits. Insulations are typically made from plastic materials such as PVC or PE.
3. Shield: The shield is a metallic layer used in some cables to protect the signals from electromagnetic interference (EMI). The shield can be woven, foil, or a combination of both.
4. Outer Jacket: The outer jacket or sheath protects the entire cable from mechanical damage, moisture, and chemicals. This jacket is usually made from durable materials like PVC or polyethylene.
Cables are categorized into different types, each designed for specific applications. Some common types of cables include:
– Power Cables: For transmitting electrical energy at various voltages (low, medium, and high voltage).
– Telecommunication Cables: For transmitting data and audio-visual signals.
– Network Cables: For connecting different devices in computer networks.
– Coaxial Cables: For transmitting radio and television signals.
– Control and Instrumentation Cables: For transmitting control signals and precise data in industrial systems.
– Audio and Video Cables: These are used to transmit audio and video signals between different devices.
– Charging and Data Transfer Cables: For charging electronic devices and transferring data between them.
Cables are used in many industries and everyday applications. From power cables supplying electrical energy in homes and industries to network cables connecting computers and other devices to the internet, cables play a vital role in modern life. Additionally, telecommunication and fiber optic cables are used for high-speed data transmission in communication networks. Audio and video cables are also used to connect playback devices and displays.
In conclusion, choosing the right cable depends on your specific needs and applications. Each type of cable has unique features and advantages that make it suitable for specific uses.
Standards related to cables include a set of technical rules and regulations designed to ensure the quality, safety, and proper performance of cables. Some important standards related to cables are:
1. IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission): International standards for electrical and electronic cables.
– IEC 60228: Standard for conductors of electrical cables.
– IEC 60502: Standard for power cables with a rated voltage of 1 kV and above.
2. IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers): Standards related to electrical cables and power distribution systems.
– IEEE 802.3: Standard for Ethernet cables.
3. UL (Underwriters Laboratories): Safety standards for cables and wires.
– UL 1581: Standard for electrical wires and cables.
4. BS (British Standards): British standards for cables.
– BS 5467: Standard for power cables with PVC insulation.
5. NFPA (National Fire Protection Association): Standards related to fire safety.
– NFPA 70 (NEC): The National Electrical Code of the United States, which includes regulations related to the installation and use of cables.
6. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): International standards for quality and management.
– ISO/IEC 11801: Standard for structured cabling in data networks.

Noavaran Tose’e Tejarat Rasta
Landline: 00982188770680
WhatsApp: 00989126835639
Telegram Channel: Sava Business Agency
Rasta Company can produce and provide high-quality products and meet your needs in this field in the best possible way.