
Water pumps use mechanical energy to extract water from a source and deliver it to a designated location. This energy can be supplied from various sources, including electricity, fossil fuels, or even human power. The operation of water pumps is based on two primary mechanisms: creating positive pressure at the pump’s outlet and negative pressure at its inlet. This pressure difference allows water to flow naturally from an area of lower pressure (the pump’s inlet) to an area of higher pressure (the pump’s outlet).
Pumps are mainly classified into two categories:
Centrifugal Pumps: These pumps use centrifugal force to propel water at high speeds through impellers. They are suitable for transferring large volumes of water at lower pressures and are commonly used in irrigation, residential systems, and industrial applications.
Positive Displacement Pumps: These pumps directly move water from one point to another using mechanical mechanisms. They are better suited for generating high pressures and are often used in situations where a small volume but high pressure is required, such as deep wells or industrial systems.
Before the advent of modern technologies, traditional and manual pumps played a crucial role in water transportation, particularly in rural areas and on a small scale. These pumps typically employed simple mechanisms that required human effort to operate.
Types of manual pumps include:
Suction Pumps: This type of pump utilizes a manual lever and piston to create suction within the pump. When the lever is moved up and down, the piston moves inside the pump cylinder, generating negative pressure. This negative pressure draws water from a source (such as a well) into the pump. Then, with the continued movement of the piston, water is expelled from the pump’s outlet. These pumps are generally effective for shallow depths (up to about 7-8 meters).
Hand-Piston Pumps: Hand-piston pumps are designed for use at greater depths than suction pumps. In this type of pump, the piston’s movement directly displaces water, mechanically lifting it from depth to the surface. Hand-piston pumps are typically used in deeper wells (up to 30 meters or more) and are more common in areas with limited access to modern energy resources.
Rotary Hand Pumps: This type of pump uses a rotating handle or wheel to pump water. By turning the handle, water is drawn into the pump and then expelled. Rotary hand pumps are suitable for transferring moderate volumes of water and are used in small agricultural or residential applications.
Treadle Pumps: Treadle pumps (or foot pumps) are another type of manual pump that operates using foot power. These pumps are particularly popular for irrigating small family farms in rural areas, as they do not require hand strength and are more efficient than traditional hand pumps. By using foot pedals, water is drawn into the pump and lifted to higher surfaces.
Despite their simplicity, traditional and manual pumps continue to be used in many parts of the world and offer several advantages:
Simple Design and Use: Manual pumps have very straightforward structures and can easily be operated by users without any specialized training. Additionally, these pumps are easy to repair and maintain.
No Need for Electricity or Fuel: One of the biggest advantages of manual pumps is that they do not require any external energy source (such as electricity or fuel) to operate. This feature makes them especially useful in remote areas without access to modern infrastructure.
Low Cost: Manual pumps have relatively low production and maintenance costs, making them an economical solution for areas with limited financial resources.
Suitable for Emergency Conditions: In situations where access to electricity is cut off or modern pump systems fail, manual pumps can serve as a backup solution.
Despite the mentioned advantages, manual pumps also have their limitations:
Dependence on Human Power: These pumps rely on human physical effort to operate, which may lead to fatigue and reduced productivity over time. Furthermore, the amount of water that can be transferred by a manual pump is limited by the physical effort exerted.
Depth and Volume Limitations: Manual pumps can typically only pump water to a certain depth (generally up to 30 meters) and are not suitable for larger volumes of water. For deeper wells or larger water needs, mechanical or electric pumps are more efficient.
Low Speed: Compared to electric pumps, manual pumps have a slower water pumping rate, which can be problematic in cases where large volumes of water need to be transferred.
Over time, with advancements in technology, electric and motor-driven pumps have replaced manual pumps in many applications. However, manual pumps are still used in areas where access to electricity or fuel is challenging. In some cases, manual pumps are kept as backups or alternative solutions in case modern systems fail.
Modern pumps utilize more advanced technologies such as electricity, fossil fuels, or even solar energy, enabling water to be transported from significant depths and in larger volumes, more quickly and efficiently.

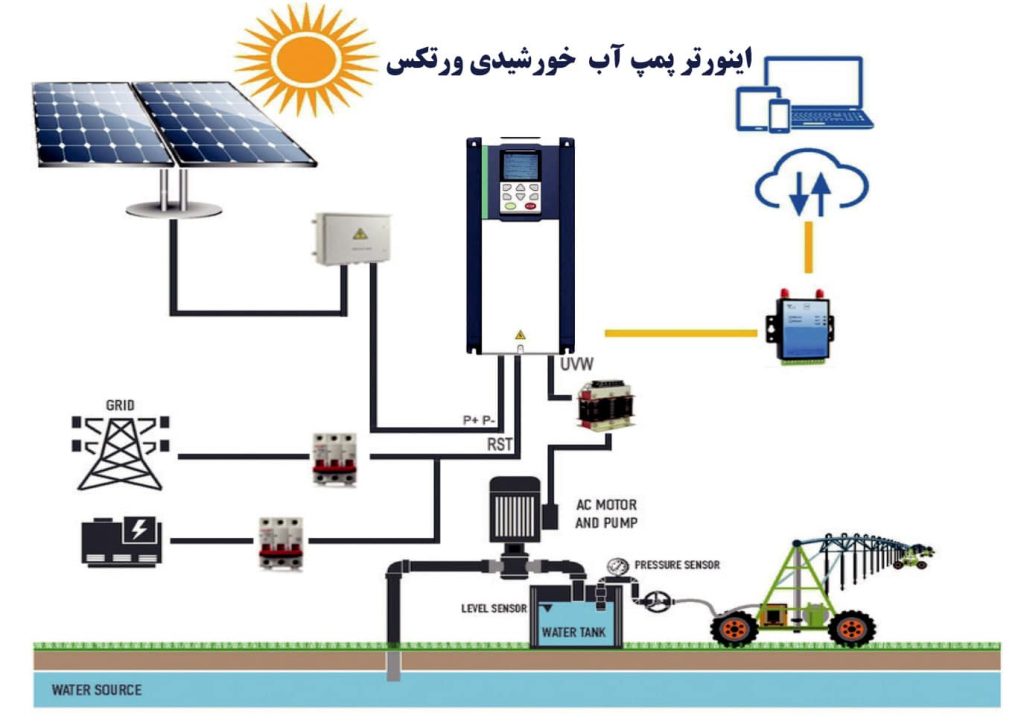

Electric pumps are a type of water pump that operates using electrical energy. These pumps are widely used in various domestic, industrial, and agricultural applications. Since electric pumps perform pumping operations automatically using electricity, they are significantly more efficient compared to manual pumps, which require human effort.
Below, we will explore the details of electric pumps, how they work, their advantages, and a comparison with manual pumps.
Electric pumps are devices that use electricity to transfer or pump water from one point to another. These pumps are connected to an electric motor that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, thereby facilitating the flow of water. Electric pumps can be used for various purposes, including extracting water from wells, supplying household water, irrigating farms, draining water from basements, and even for industrial applications.
Electric pumps typically consist of two main components: an electric motor and an impeller or pumping mechanism.
Electric Motor:
The electric motor is the heart of the electric pump. This motor receives electrical energy from a power source (the municipal power grid or a generator) and converts it into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then transferred to the pump’s impeller.
Impeller or Pumping Mechanism:
The pump’s impeller (or any other type of mechanism in various pumps) begins to rotate, creating a pressure differential within the pump that allows water to flow from the inlet (with lower pressure) to the outlet (with higher pressure). In centrifugal pumps, this is achieved through centrifugal force, while positive displacement pumps utilize piston or gear mechanisms.
Electric pumps offer several significant advantages compared to manual and other types of pumps:
High Efficiency and Speed:
Electric pumps operate automatically using electric power, eliminating the need for human effort to start or continuously maintain them. They can pump large volumes of water in a short time, making them suitable for wide-ranging applications such as agricultural irrigation, urban water supply, and industrial use.
Reduced Human Labor:
Manual pumps require human effort to operate, while electric pumps completely eliminate this need. All that is required is to connect the pump to electricity, and it will automatically perform water pumping. This increases productivity and reduces user fatigue.
Capability for Greater Depths and Distances:
Electric pumps can extract water from significant depths and over long distances. Especially in deep wells or projects that require water transfer to remote areas, electric pumps can operate with high power and pressure, whereas manual pumps are not suitable for such depths or long distances.
Precision in Pressure and Flow Control:
Electric pumps are usually equipped with advanced control systems that can accurately adjust water pressure and flow. This feature is essential in situations where a constant flow or specific pressure is required (such as in drip irrigation systems or urban water supply).
Variety in Power and Size:
Electric pumps are produced in various types and power levels, suitable for applications ranging from small household needs to large industrial and agricultural projects. This variety allows users to select a pump that meets their specific needs.
Lower Operational Costs in the Long Term:
Although the initial installation cost of electric pumps may be high, their operational costs are generally lower than manual pumps due to their automation and high efficiency. Additionally, electric pumps require less maintenance and repairs, contributing to cost savings.
Despite their many advantages, electric pumps also have some drawbacks:
Dependence on Electricity:
Electric pumps require power to operate. In case of power outages or lack of access to the power grid, these pumps cannot function. This issue can be problematic in areas where the power supply is unstable or subject to frequent outages.
Higher Initial Costs:
Installing an electric pump incurs higher initial costs compared to manual pumps. In addition to the pump itself, connecting to the power grid or installing a generator can also be expensive.
Sensitivity to Environmental Conditions:
Electric pumps need protection from environmental conditions. They must be installed in locations that protect them from water, dust, and temperature changes. Moreover, they require extra protection in areas with high humidity or heavy rainfall.
Efficiency and Power:
Electric pumps are significantly more powerful than manual pumps and can pump larger volumes of water in a shorter time. Manual pumps are suitable for small, household applications, while electric pumps can be used in larger projects such as farm irrigation or urban water supply.
Human Labor Requirement:
Electric pumps operate fully automatically and do not require human effort for startup or continuous operation. Manual pumps require physical exertion, making long-term use tiresome.
Speed and Efficiency:
Electric pumps operate much faster, capable of transferring large amounts of water per hour. Manual pumps, due to their reliance on human effort, are slower and only suitable for small volumes of water.
Depth and Distance Limitations:
Electric pumps can transfer water from deep wells and over long distances. Manual pumps are only efficient at limited depths (typically 7 to 10 meters) and are not suitable for transferring water over long distances.
Cost:
Manual pumps have lower initial and maintenance costs but require human labor, which can reduce long-term efficiency. Electric pumps have higher initial costs but reduce operational and labor costs in the long run.
Electric pumps are used in various applications:
Residential:
In household water supply systems, they are used to move water from shallow wells or water tanks into homes.
Agricultural:
For irrigating large farms, utilizing drip or sprinkler irrigation systems, and extracting water from deep wells.
Industrial:
Electric pumps are used in various industries to transfer water, chemicals, or other fluids. They are particularly common in oil and gas industries, treatment plants, and power stations.
Municipal:
Electric pumps play a key role in municipal water supply systems and draining rainwater from streets and basements.
Novaran Tose’e Tejarat Rasta is one of the leading manufacturers and suppliers of water pumps in Iran. The company leverages state-of-the-art technologies and a specialized team to produce high-quality and reliable products that have widespread applications across various sectors, including agriculture, residential, industrial, and urban environments.
In addition to meeting domestic needs, Novaran Tose’e Tejarat Rasta plays a significant role in international markets by exporting its pumps worldwide. By adhering to global standards and a commitment to innovation, the company has successfully earned customer satisfaction in different countries, exporting its products to regions including Europe, Asia, and Africa.
A commitment to quality, strong after-sales service, and robust support have made Novaran Tose’e Tejarat Rasta one of the most reputable names in the pump manufacturing industry.

For inquiries, purchasing, or more information about our products, please reach out to us using the contact details below:
– Phone: +98 21 8877 0680
– WhatsApp: +98 912 6835 639
– Telegram Group: SAVA Business Group
Our team is dedicated to providing excellent support and is ready to assist with any questions or needs you may have.